The future of work
Education for tomorrow’s modern workforce
The American Society of Mechanical Engineers and Autodesk led a multiphase research project that revealed a divide between education programs and manufacturing industry workforce needs.
Building blocks for Industry 4.0

An industry in transition
The resulting Future of Manufacturing white paper indicates that the manufacturing industry of tomorrow will require more than new technology. As companies face increased demands for more sophisticated products while navigating resource scarcity, and supply chain disruptions, they will need a highly skilled and adaptive workforce.

Keeping pace with industry expectations
Manufacturing innovations are unlocking unprecedented productivity, quality, and reductions in waste and cost. These innovations are revealing outdated education programs and their limitations. This has triggered movement around curriculum updates and project-based learning. Educators can take steps to mitigate the impending risk and prepare students for the modern workforce.
New skills for Industry 4.0
Many of today's manufacturing skills were built for Industry 3.0 or earlier. Building curricula designed for Industry 4.0 will develop the skills, technical knowledge, and workflow experience students require for the modern manufacturing landscape.
-

Technical/hard skills
To keep pace with Industry 4.0 advancements, tomorrow's workforce will need a broad range of advanced technological skills.
-

Soft skills
As digital transformation efforts drive convergence across manufacturing roles and workflows, collaboration, communication, and problem-solving are becoming ever-critical.
-

Interdisciplinary skills
As collaboration requirements increase, so does the need for a better understanding of each functional role across the manufacturing process.

Mechanical Engineers
Tomorrow's mechanical engineers will play expanded roles in developing products that are designed for manufacturability and are leaner, smarter, and more sustainable.
Technical/hard skills: AI/ML; design for manufacturing; generative design; coding/programming; 3D modeling and design; data analytics and visualization; prototyping; engineering simulation and digital twin
Manufacturing Engineers
Tomorrow's manufacturing engineers will design and implement manufacturing systems to improve time-to-market while reducing cost, waste, and defects.
Technical/hard skills: CNC machining, AI/ML; design for manufacturing; robotics/cobotics; integrated CAD/CAM software and programming; additive and hybrid manufacturing; operations technology; AR/VR
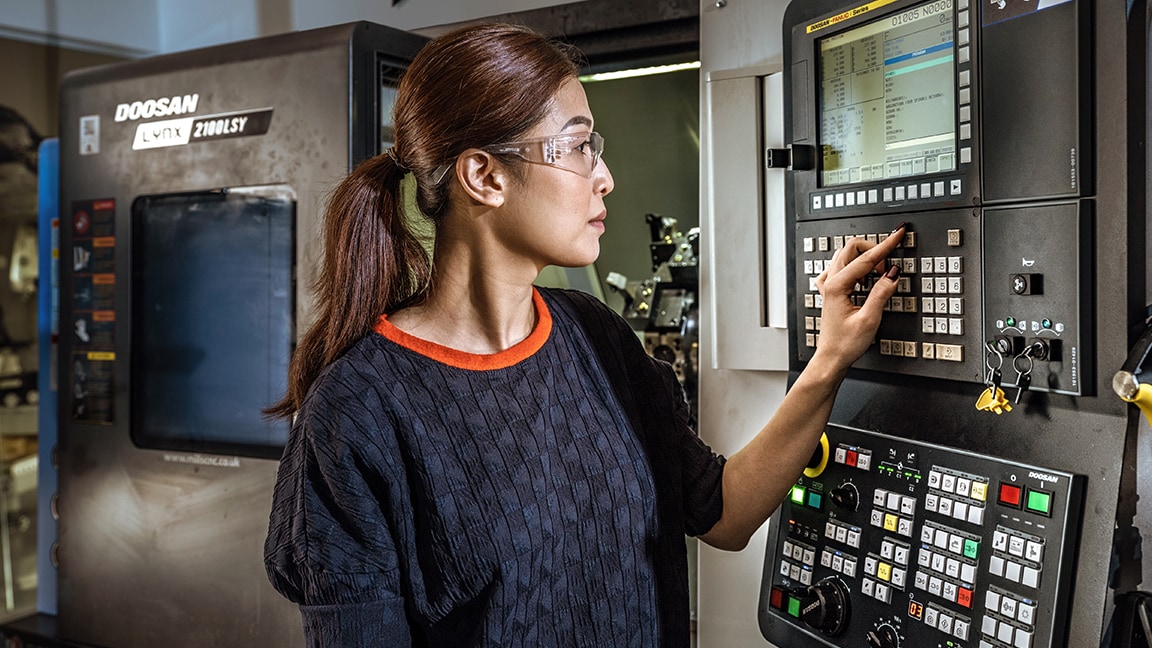

CNC Machinists
Educators are positioned to help machinists prepare and evolve to an elevated role that includes managing and programming advanced technology.
Technical/hard skills: AI/ML; robotics/cobotics; integrated CAD/CAM software and programming; additive and hybrid manufacturing; predictive/preventative maintenance; five-axis or higher machine tools
-
Purdue University Bechtel Innovation Design Center
The Bechtel Innovation Design Center at Purdue University uses Fusion 360 as part of a teaching environment that mimics a commercial Industry 4.0-adopted shop.
-
ITE College of Central Singapore
The ITE College mechanical engineering program is giving students a competitive edge in the job market. With lesson plans built on Fusion 360, students rapidly progress from designing products to manufacturing them.
Reshape your curriculum for the modern industry
Learn more
Read the e-book or full market research report for more details about Industry 4.0 skills requirements and the role educators play in building tomorrow's workforce.
Take the next step
Ready to discover new skills training to update your curriculum and align with industry needs? Schedule a fully funded workshop or download Fusion 360 for educators at no cost.